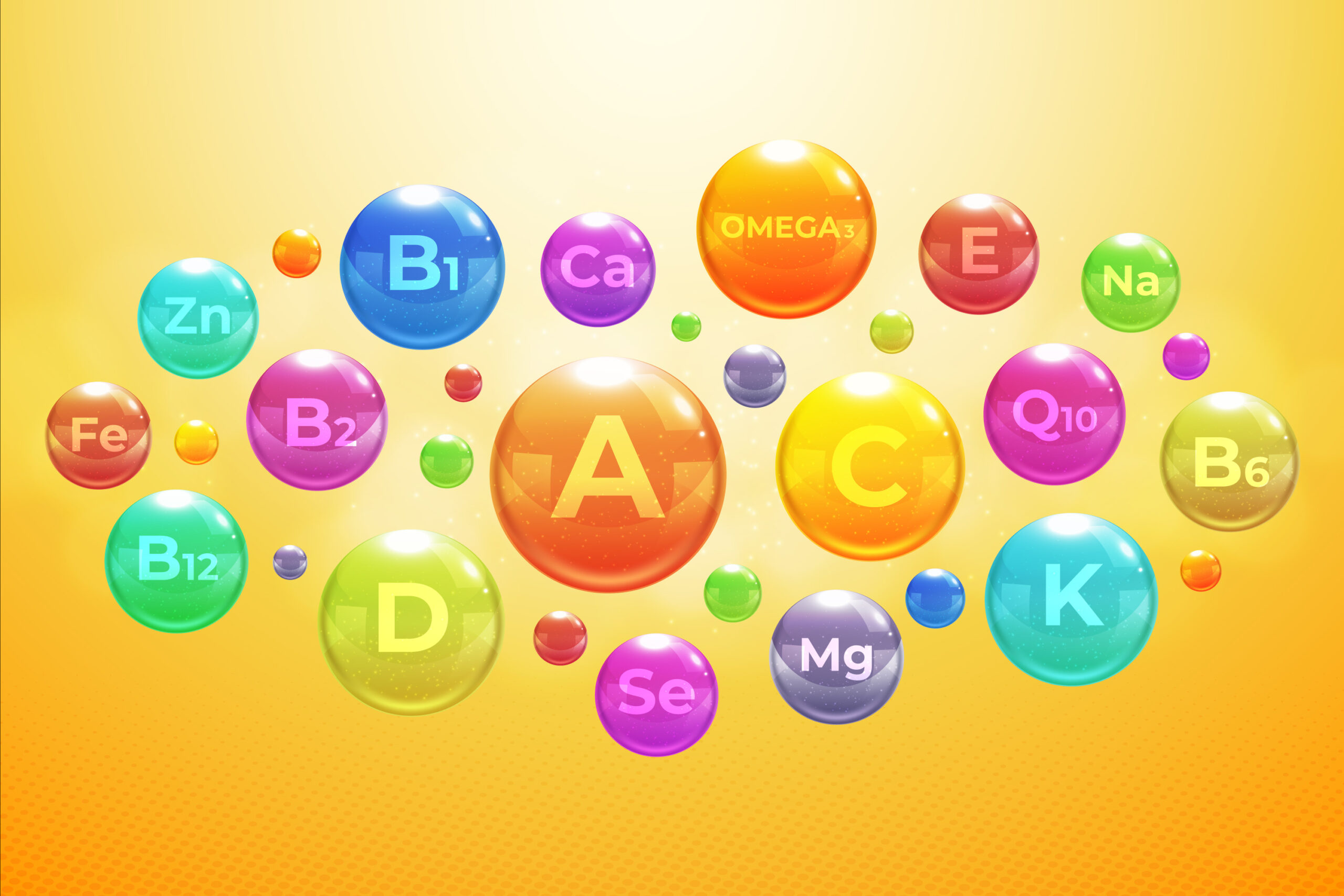
Vitamins are essential organic compounds that are required in small amounts for various physiological functions in the body. They play crucial roles in metabolism, growth, immunity, and overall health. Vitamins are classified into two main categories based on their solubility:
Fat-Soluble Vitamins:
These vitamins dissolve in fat and are stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver. They are:
Vitamin A: Found in liver, dairy products, and orange/yellow fruits and vegetables.
Vitamin D: Synthesized by the skin in response to sunlight and found in fatty fish and fortified foods.
Vitamin E: Found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
Vitamin K: Found in green leafy vegetables, liver, and soybean oil.
Water-Soluble Vitamins:
These vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored in the body for long periods. They include:
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid): Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
B Vitamins (Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid, Pyridoxine, Biotin, Folate, Cobalamin):
Thiamin (B1): Found in whole grains, and legumes.
Riboflavin (B2): Found in dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and eggs.
Niacin (B3): Found in meat, fish, and whole grains.
Pantothenic Acid (B5): Found in meat, avocados, and whole grains.
Pyridoxine (B6): Found in meat, fish, and bananas.
Biotin (B7): Found in eggs, nuts, and cauliflower.
Folate (B9): Found in leafy greens, legumes, and fortified grains.
Cobalamin (B12): Found in animal products like meat, fish, and dairy.
Food Supplements refer to products that contain vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes, herbs, or other botanicals intended to supplement the diet. These supplements come in various forms like pills, capsules, powders, and liquids, and are often consumed to address specific nutritional deficiencies or to promote overall health. Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet, but they can be beneficial when dietary intake is insufficient or when specific health conditions require additional nutrients.
Examples of common food supplements include multivitamins (which contain a combination of various vitamins and minerals), omega-3 fatty acids (often sourced from fish oil), calcium and vitamin D supplements for bone health, iron supplements for treating anemia, and probiotics for gut health, among others.
Disclaimer: This article is meant for information and should not be used as medical advice, please consult your physician for your condition or before using any medications.